Posted on
MMSA’s Smart Greenhouses project brings curriculum from the Boston College Lynch School of Education and Human Development(opens in a new tab) to Maine students.
One aspect of this transdisciplinary project is computer programming. In order to make the process of learning to code more accessible to participants, block coding software is used. This resource walks through the process of assessing block coding projects, a concept that was also shared on MMSA’s blog, which includes descriptions of the specific tools used in the context of the project.
The following tips can be applied generally to block coding assessment.
Take advantage of the visual nature of block coding. Both students and teachers alike can easily display programs written with block coding software. This is useful for walking an entire class through an exercise, not to mention as a way for students to demonstrate a program in process.
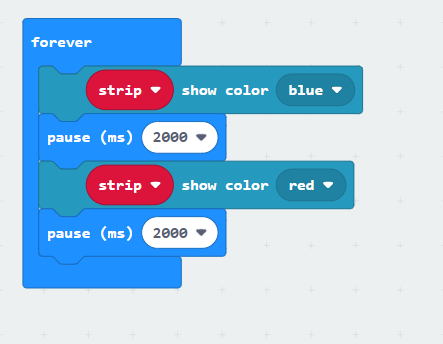
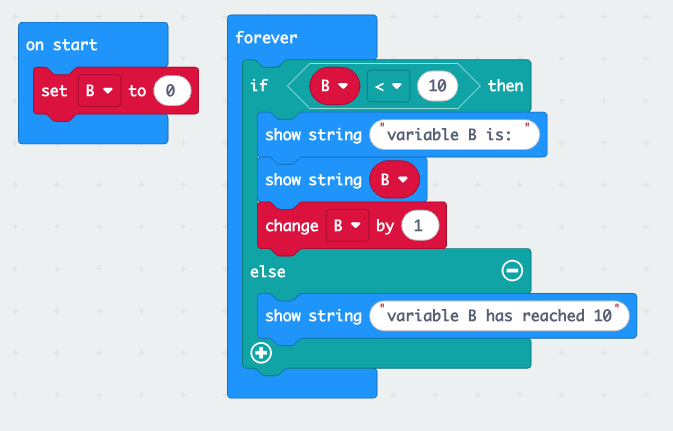
Quizzes are easy to implement alongside block coding instruction. Building on the previous tip, the visual aspects of block coding lend it to easily incorporating into quiz questions. The following are a few examples of how questions could be set up with screenshots from the coding application:
Commenting code makes assessment simpler and is a crucial skill to develop. Commenting code is not only a best practice in general, it also makes the person writing the code stop and think about how their code works in order to explain it for someone else to understand. Obviously this is helpful to the coder themselves and anyone else who will later work with their code. But it is also a way of assessing student knowledge. It’s one thing to write code that accomplishes something, but another thing entirely to understand why it functions the way it does.
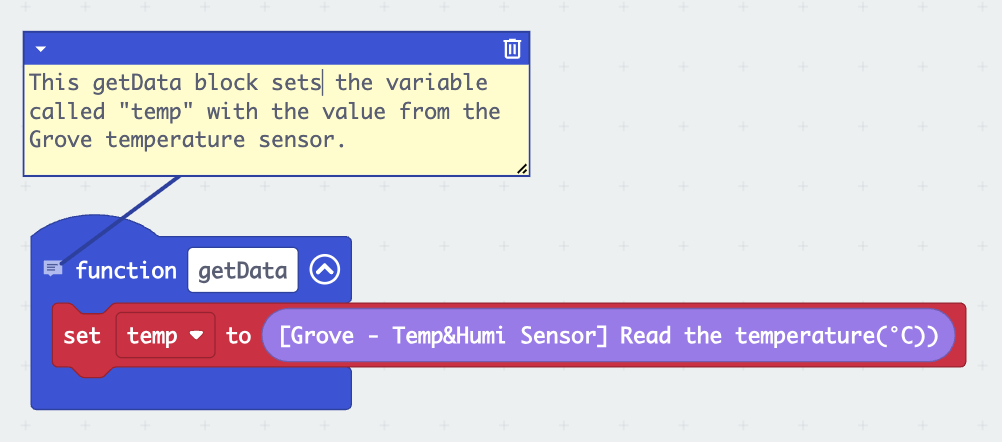
Another bonus of regularly commenting code for beginners is that it reveals ways in which code could be simplified, leading to opportunities to learn to produce cleaner, leaner, and, as a result, more performant and legible code.
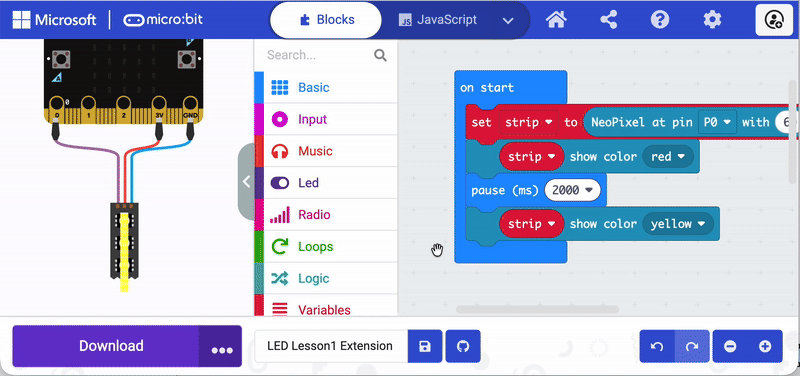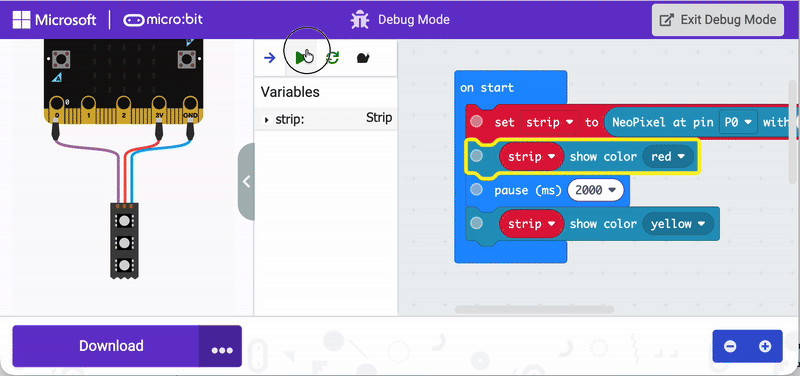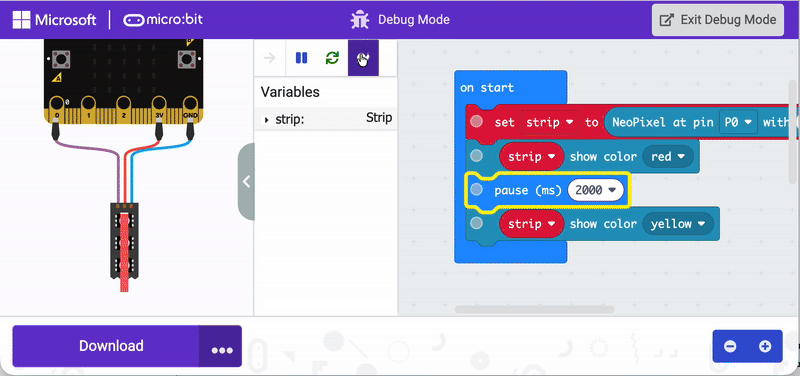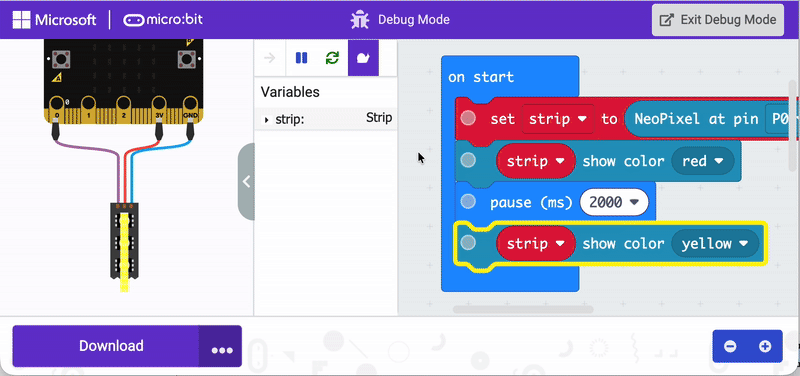
Use debug mode to visualize where code works—and where it doesn’t. Visual coding applications have a debug mode that can run through code and indicate how it functions. The animation below shows how this works in the MakeCode application specifically.
Related Staff

STEM Education Specialist